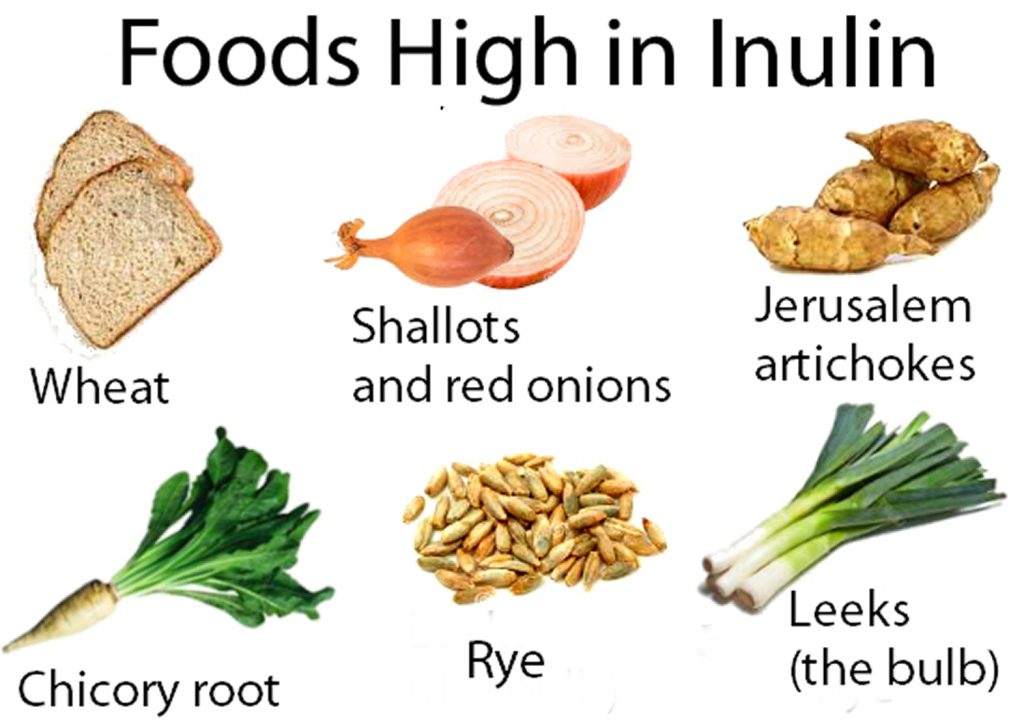
Inulin is a type of soluble fiber and prebiotic found naturally in a variety of fruits, vegetables, and herbs, such as chicory root, onions, garlic, bananas, and asparagus. It is not digested or absorbed in the stomach, making its way to the colon where it serves as a food source for beneficial gut bacteria. This helps support the growth and activity of healthy microorganisms in the intestines, contributing to improved digestive health. Inulin is also used in dietary supplements for various health benefits, including promoting gut health, alleviating constipation, and potentially aiding in weight management and blood sugar control. Despite its potential, scientific evidence on the long-term benefits of inulin for conditions like obesity and diabetes remains inconclusive. When consumed in adequate amounts, inulin is generally considered safe for most people, though it can cause gastrointestinal discomfort such as bloating and gas in some individuals. It is typically used in supplement form in doses ranging from 10 to 40 grams per day. Before adding inulin to your routine, especially for those with underlying health conditions or on medications, consulting a healthcare provider is recommended.
What is Inulin?
Inulin is a type of soluble dietary fiber that belongs to a class of carbohydrates known as fructans. It is found naturally in a variety of fruits, vegetables, and herbs, including chicory root, onions, garlic, bananas, leeks, and asparagus. Inulin is unique because, unlike most other carbohydrates, it is not digested or absorbed in the stomach. Instead, it passes into the large intestine, where it acts as a prebiotic, providing nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. This action helps to maintain a healthy balance of the microbiome, promoting optimal digestive health and overall well-being.
Inulin is often extracted from chicory roots and used in dietary supplements for its potential health benefits. These include improving gut health, alleviating constipation, supporting weight loss, and possibly helping to regulate blood sugar levels. Some studies suggest that inulin may assist with blood lipid management, such as lowering cholesterol and triglycerides, though more research is needed to confirm these effects. Inulin is also valued for its ability to enhance the texture and taste of low-fat or sugar-free products due to its mildly sweet flavor.
While inulin is generally considered safe when consumed in food, higher doses in supplement form can lead to side effects like bloating, gas, and abdominal discomfort. As a fiber supplement, inulin should be gradually introduced into the diet to avoid digestive issues. Consulting a healthcare provider is advisable before using inulin for specific health concerns or alongside medications.
How Inulin Works?
Inulin works primarily as a prebiotic fiber, meaning it serves as food for beneficial bacteria in the gut. Unlike other carbohydrates, inulin is not digested or absorbed in the small intestine. Instead, it travels to the large intestine, where it is fermented by gut microbiota. This fermentation process helps to promote the growth and activity of healthy bacteria, particularly Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, which are crucial for maintaining a balanced gut microbiome.
The increase in beneficial gut bacteria can have several positive effects on health, such as improved digestion, better immune function, and enhanced nutrient absorption. As inulin is fermented, it produces short-chain fatty acids like butyrate, which play a key role in supporting the health of the gut lining and reducing inflammation.
Inulin also aids in regulating bowel movements, as it helps to soften stools and increase their bulk, making it useful for managing constipation. Additionally, inulin may help with weight management by promoting satiety, as it absorbs water and forms a gel-like substance in the digestive tract, potentially reducing appetite. Some studies suggest that inulin may assist in managing blood sugar levels by slowing the absorption of glucose, providing a more gradual rise in blood sugar after meals.
Due to its ability to support gut health and offer digestive benefits, inulin is increasingly used as an ingredient in functional foods and dietary supplements. However, as a fiber, it should be introduced gradually to avoid digestive discomfort.
Importance of Inulin
Inulin plays a significant role in supporting overall digestive health, making it an important component of a balanced diet. As a prebiotic fiber, it promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, which are essential for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. A balanced microbiome is linked to improved digestion, enhanced immune function, and better nutrient absorption. Inulin’s fermentation in the large intestine produces short-chain fatty acids like butyrate, which help nourish the cells of the colon, reduce inflammation, and improve gut integrity.
Inulin is also important for managing bowel regularity, as it helps alleviate constipation by increasing stool bulk and softening stools. This can provide relief for individuals suffering from chronic constipation or irregular bowel movements. Beyond its digestive benefits, inulin has been shown to potentially support weight management. It may enhance feelings of fullness by absorbing water and forming a gel-like substance, which can help reduce overall calorie intake.
Additionally, inulin may offer metabolic benefits, such as improving blood sugar control by slowing the absorption of glucose. This makes it a potential ally in managing diabetes and supporting heart health by regulating cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Inulin’s low glycemic index makes it a suitable dietary addition for individuals looking to control blood sugar levels.
Overall, inulin is a versatile and beneficial fiber that supports gut health, digestive function, and metabolic balance, making it an important addition to a healthy diet.
Role of Inulin
Inulin plays a crucial role in promoting digestive health and maintaining overall well-being due to its function as a prebiotic fiber. As a prebiotic, inulin provides nourishment to beneficial bacteria in the gut, which are essential for a balanced microbiome. This helps improve gut health by encouraging the growth of good bacteria like Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, which aid in digestion, immune function, and the absorption of nutrients. Additionally, inulin’s fermentation process in the large intestine produces short-chain fatty acids, particularly butyrate, which nourish the gut lining, reduce inflammation, and support the health of colon cells.
Beyond its digestive benefits, inulin plays a role in managing constipation by increasing stool bulk and improving bowel regularity. It helps soften stools, making them easier to pass, and thus provides relief for individuals dealing with chronic constipation. Inulin may also support weight management, as it can increase feelings of fullness and reduce appetite by absorbing water and forming a gel-like substance in the stomach. This can lead to lower overall calorie intake, contributing to short-term weight loss.
Moreover, inulin has the potential to help regulate blood sugar levels by slowing the absorption of glucose, making it a beneficial addition to the diets of individuals with diabetes or those seeking to prevent blood sugar spikes. It also has potential heart-health benefits, as it may assist in lowering cholesterol and triglyceride levels, improving overall cardiovascular health.
Function of Inulin
Inulin functions primarily as a prebiotic fiber, meaning it serves as a food source for beneficial bacteria in the gut. Once consumed, inulin is not digested in the stomach or small intestine. Instead, it travels to the large intestine, where it undergoes fermentation by gut microbiota. This fermentation process helps promote the growth of good bacteria, such as Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, which are crucial for maintaining a balanced gut microbiome. A healthy microbiome supports proper digestion, enhances nutrient absorption, and boosts immune function.
Inulin also plays a key role in improving bowel regularity. It helps to increase stool bulk, softens stools, and promotes more frequent bowel movements, making it an effective remedy for constipation. In individuals with digestive discomfort, such as bloating or irregular bowel patterns, inulin can help restore normal digestive function.
Additionally, inulin helps manage appetite and supports weight management. By absorbing water and forming a gel-like substance in the stomach, it increases feelings of fullness, which can help reduce overall calorie intake and support weight loss efforts. Furthermore, inulin has been shown to regulate blood sugar levels by slowing glucose absorption, making it particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those looking to control blood sugar spikes after meals. It may also have cardiovascular benefits, such as lowering cholesterol and triglyceride levels, contributing to heart health.
Benefits of Inulin
Promotes Gut Health
Inulin acts as a prebiotic fiber that feeds beneficial bacteria in the gut, promoting the growth of good bacteria like Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli. This helps improve digestion and overall gut health, supporting a balanced microbiome.
Improves Bowel Regularity
Inulin enhances stool bulk and softens stools, which can help alleviate constipation and promote more regular bowel movements. This makes it effective for those with digestive issues.
Supports Weight Management
By absorbing water and forming a gel-like substance in the stomach, inulin increases feelings of fullness, which can help reduce appetite and lower overall calorie intake, potentially aiding in weight loss.
Regulates Blood Sugar Levels
Inulin may help manage blood sugar by slowing the absorption of glucose, leading to a more gradual rise in blood sugar after meals. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those looking to control blood sugar spikes.
Enhances Mineral Absorption
Inulin aids in the absorption of important minerals, particularly calcium and magnesium, improving bone health and reducing the risk of deficiencies.
Side Effects of Inulin
Gastrointestinal Discomfort
One of the most common side effects of inulin is gastrointestinal discomfort. This can include bloating, gas, and cramps, particularly when taken in large doses. The fermentation of inulin by gut bacteria can produce gas, which may lead to these symptoms.
Diarrhea
High doses of inulin may cause diarrhea in some individuals. As a soluble fiber, it can speed up intestinal transit time, leading to more frequent or loose stools.
Constipation
Inulin may cause constipation in some individuals, especially when not introduced gradually into the diet. The fiber can sometimes absorb too much water and slow down digestion, leading to harder stools.
Abdominal Distension
Some people experience abdominal distension or a feeling of fullness after consuming inulin, which can be uncomfortable. This is a result of inulin’s fermentation in the gut, which can produce gas and cause bloating.
Potential Allergic Reactions
Although rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to inulin. Symptoms may include itching, rash, or more severe reactions like difficulty breathing, in which case medical attention should be sought immediately.
Pros and Cons of Inulin
Pros
Supports Digestive Health
Inulin is an effective prebiotic that helps promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. This contributes to a healthier gut microbiome, which can improve digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall digestive function.
Aids in Weight Management
Inulin can help manage weight by increasing feelings of fullness. When consumed, it absorbs water and forms a gel-like substance in the stomach, which helps curb appetite and reduce calorie intake. This can be particularly beneficial for those looking to lose or maintain weight.
Improves Bowel Regularity
As a soluble fiber, inulin adds bulk to stools and helps soften them, improving bowel regularity and relieving constipation. It supports overall gut motility, making it useful for individuals with irregular bowel movements.
Regulates Blood Sugar Levels
Inulin can help lower blood sugar levels by slowing glucose absorption in the digestive tract. This can prevent blood sugar spikes after meals and may be especially helpful for people with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
Enhances Mineral Absorption
Inulin has been shown to improve the absorption of essential minerals like calcium and magnesium, which are important for bone health. This can contribute to stronger bones and a reduced risk of mineral deficiencies.
Cons
Gastrointestinal Discomfort
One of the most common downsides of inulin is its potential to cause gastrointestinal issues such as bloating, gas, and abdominal cramps. These symptoms are more likely to occur when inulin is consumed in high doses.
Risk of Diarrhea
Inulin can sometimes lead to diarrhea, especially when taken in large quantities. As a fiber, it may speed up digestion and cause more frequent or looser stools in some individuals.
Constipation in Some Cases
Although inulin generally helps with constipation, it can cause constipation in certain individuals, particularly when not gradually introduced into the diet or when taken in excessive amounts.
Possible Allergic Reactions
While rare, some people may experience allergic reactions to inulin, which can include skin rashes, itching, or even difficulty breathing. If an allergic reaction occurs, immediate medical attention is necessary.
Interaction with Medications
Inulin can interact with certain medications, particularly those used to manage diabetes. It may lower blood sugar levels too much when combined with antidiabetic drugs, which requires close monitoring of blood glucose levels.
FAQs for Inulin
1. What is inulin, and how does it work?
Inulin is a type of prebiotic fiber found in various fruits, vegetables, and herbs. It is not digested in the stomach and instead reaches the large intestine, where it helps nourish beneficial bacteria in the gut. This supports a healthy microbiome, improves digestion, and can aid in various digestive issues like constipation.
2. What are the health benefits of inulin?
Inulin has several health benefits, including promoting gut health, improving bowel regularity, and supporting weight management by increasing feelings of fullness. It may also help regulate blood sugar levels, improve mineral absorption (like calcium), and assist in lowering cholesterol and triglyceride levels, supporting cardiovascular health.
3. Are there any side effects of inulin?
Inulin is generally safe when consumed in food amounts, but high doses can cause gastrointestinal discomfort, including bloating, gas, cramps, and diarrhea. Some people may also experience constipation or abdominal distension. It’s important to start with small doses and increase gradually to avoid these side effects.
4. How much inulin should I take daily?
The typical daily dose of inulin varies depending on the individual and their health goals. Generally, 10-40 grams per day is considered safe for most people. It’s recommended to start with a smaller amount, especially for those who are new to fiber supplements, to minimize digestive discomfort.
5. Can inulin help with weight loss?
Yes, inulin may support weight loss by increasing satiety. As a soluble fiber, it absorbs water and forms a gel-like substance in the stomach, which can help reduce hunger and control appetite. However, its effects on long-term weight loss are still being studied, and it should be used in combination with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
